Deploying with Kubernetes
Posted on Thu 26 November 2020 in Software • 4 min read
Following on with previous posts on this blog. This post will be going through how to deploy our fibonacci application we previously built in a Kubernetes cluster. To reiterate we will be using the following technologies:
| Technology | Use |
|---|---|
| Docker | Docker will be used to containerization of the services inside our app |
| Vue | Vue is the front-end JavaScript framework that we will use |
| Google Cloud | The cloud provider that will host our Kubernetes cluster |
| Express | Express is responsible for the API between Redis, PostgreSQL and Vue |
| Redis | Redis will store/retrieve any local data used by our users |
| PostgreSQL | PostgreSQL will be our database |
| Nginx | Nginx will handle the routing between our services |
| Github Actions | The CI/CD for our project |
This post is apart of a series on Docker/Kubernetes, find the other posts at:
- Intro to Docker
- Develop and Develop with Docker
- Develop and Develop Multi Container Applications
- Intro to Kubernetes
- Developing with Kubernetes
- Deploy a Node Web App to AWS Elastic Beanstalk with Docker
Previously we made use of services provided by AWS for Redis & PostgreSQL, in this post these services will be run inside their own pods.
The Architecture
To make our application run on Kubernetes, we need to make a few changes. In essence though the architecture will
The above chart was made with mermaid.js.
See the following posts for developing in different contexts:
- Container context: Develop and Develop Multi Container Applications
- Kubernetes context: Developing with Kubernetes
Cloud Provider
To deploy our Kubernetes cluster, we need a cloud provider, for this post we will be using Google Cloud. Other options are:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Digital Ocean
- Microsoft Azure
- Many more
Google Cloud
Now that we've logged into our Google Cloud console, we create a new project, enable billing and then head to Kubernetes Engine. This will go through some one time set up to enable the Kubernetes Engine API for our project and upon completion we can create a cluster. As soon as we hit Create Cluster, this begins the billing so be careful!
Service Account
Before moving onto the next step, we need to authorize Github Actions to be able run inside the cluster on Google Cloud. This is done by creating a service account, exporting the keys as JSON and storing it as a secret within the repository on Github.
CI/CD
For our CI/CD we will be using GitHub Actions. Github Actions are free to public repositories, and I presented at PyconAU 2020 on the topic, find the recording at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aBjzZkaGhU&feature=emb_logo.
Let's get into setting up the action for this project, we will be aiming to achieve a few things in this action:
- Initialise & configure the Google Cloud SDK
- Login to Docker Hub so we can push our images up
- Build our application and run tests
- Build and tag images ready to be pushed to Docker Hub
- Push our tagged images to Docker Hub
- Update the Kubernetes configuration on Google Cloud
To see the full configuration which achieves this head to: https://github.com/JackMcKew/multi-docker/blob/master/.github/workflows/google-cloud-cluster.yaml.
We make sure to use the ${GITHUB_SHA}, when we're tagging our images versions, this is due to ensure that our kubernetes cluster ensures to update the images when we are running kubectl apply -f k8s. If we didn't add the SHA, they would be all tagged with :latest, and kubernetes wouldn't see an update.
Make sure to update the cluster id in the command
gcloud container clusters get-credentials my-first-cluster-1with the cluster desired to update the kubernetes configuration, otherwise there'll be errors.
Once this action has successfully completed, we can head to the Workloads page of our project and we should be able to see all the deployment configurations that we set up to be deployed.
Setting up Ingress-Nginx
Before we can access our application through an IP or web address, we need to set up ingress-nginx, similar to how we did with docker-compose in previous posts. Luckily, we can make use of helm to add this functionality for us (provided we'd set up nginx configuration like we already have). This can be done by sshing into the terminal of our Kubernetes cluster, or similarly making use of the Cloud Shell provided by Google Cloud.
Firstly which we need to install helm (https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/#from-script):
1 2 3 | |
Followed by setting up ingress-nginx (https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/deploy/#using-helm):
1 2 | |
Success
Now we head to our Services & Ingress page in our project, where we can see all the pods that are used for hosting endpoints. Provided the ingress-nginx service has been created, there should be a External Load Balancer service with an IP, that we can access. Heading to this IP will lead us to our application!
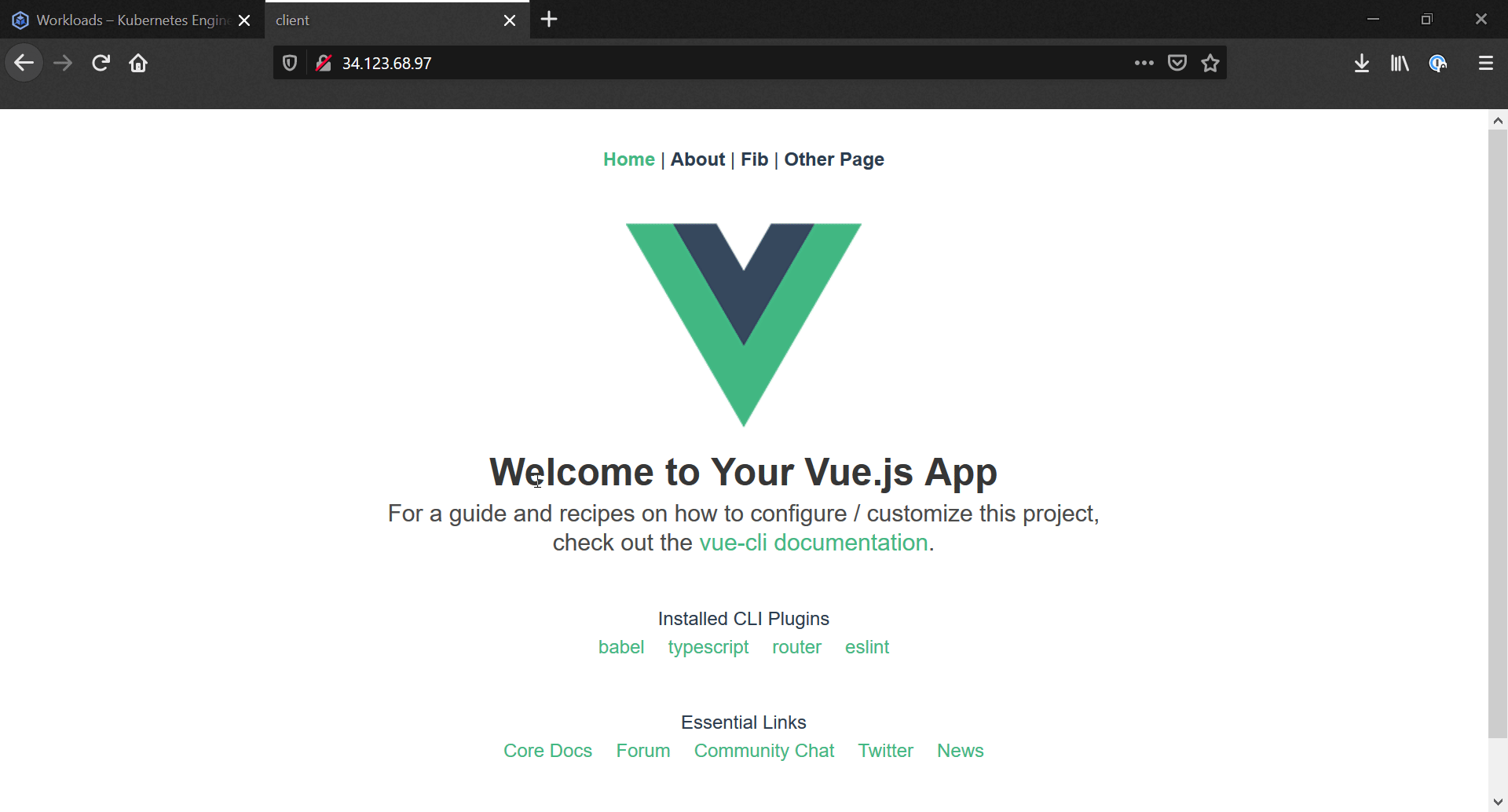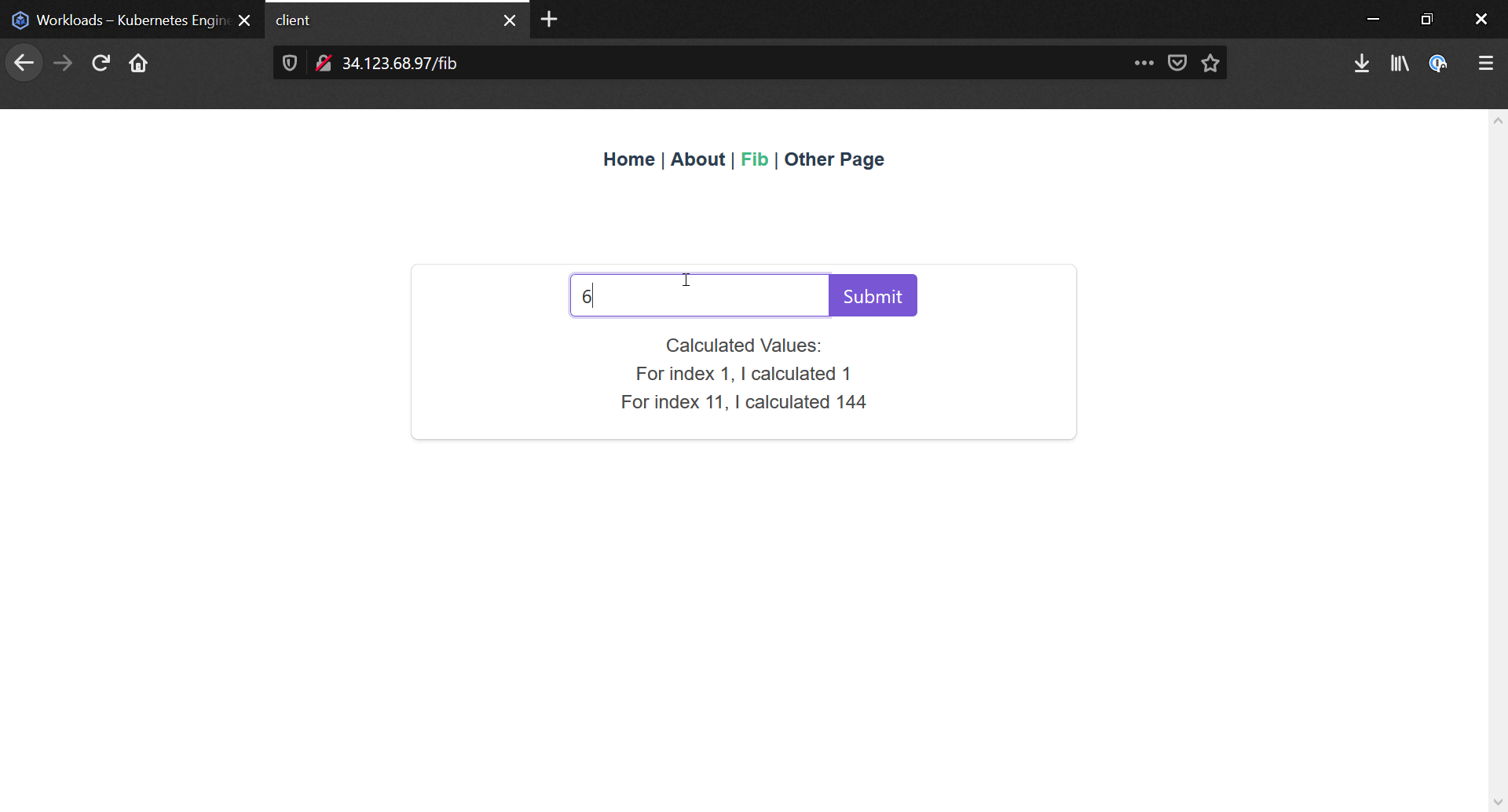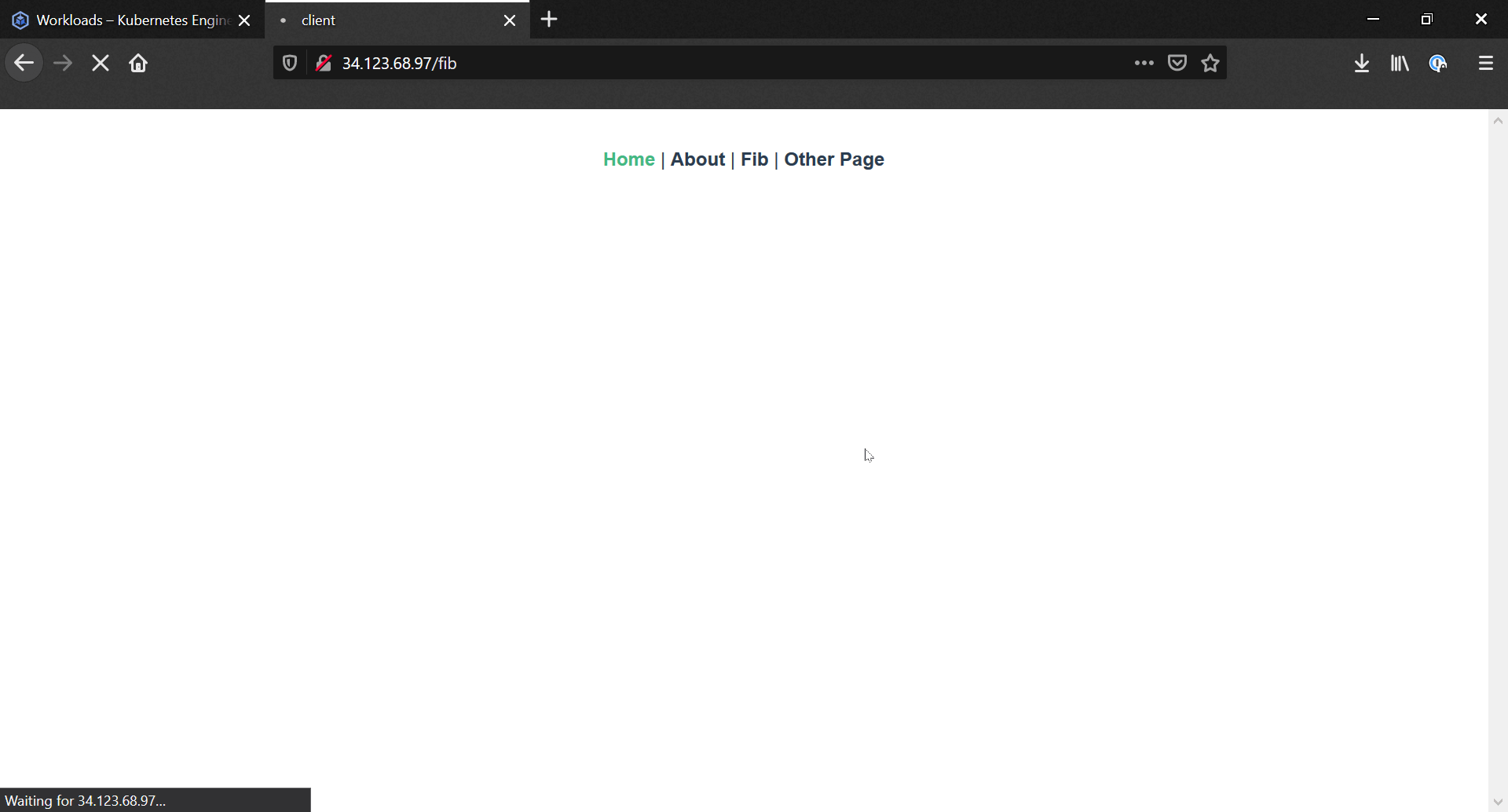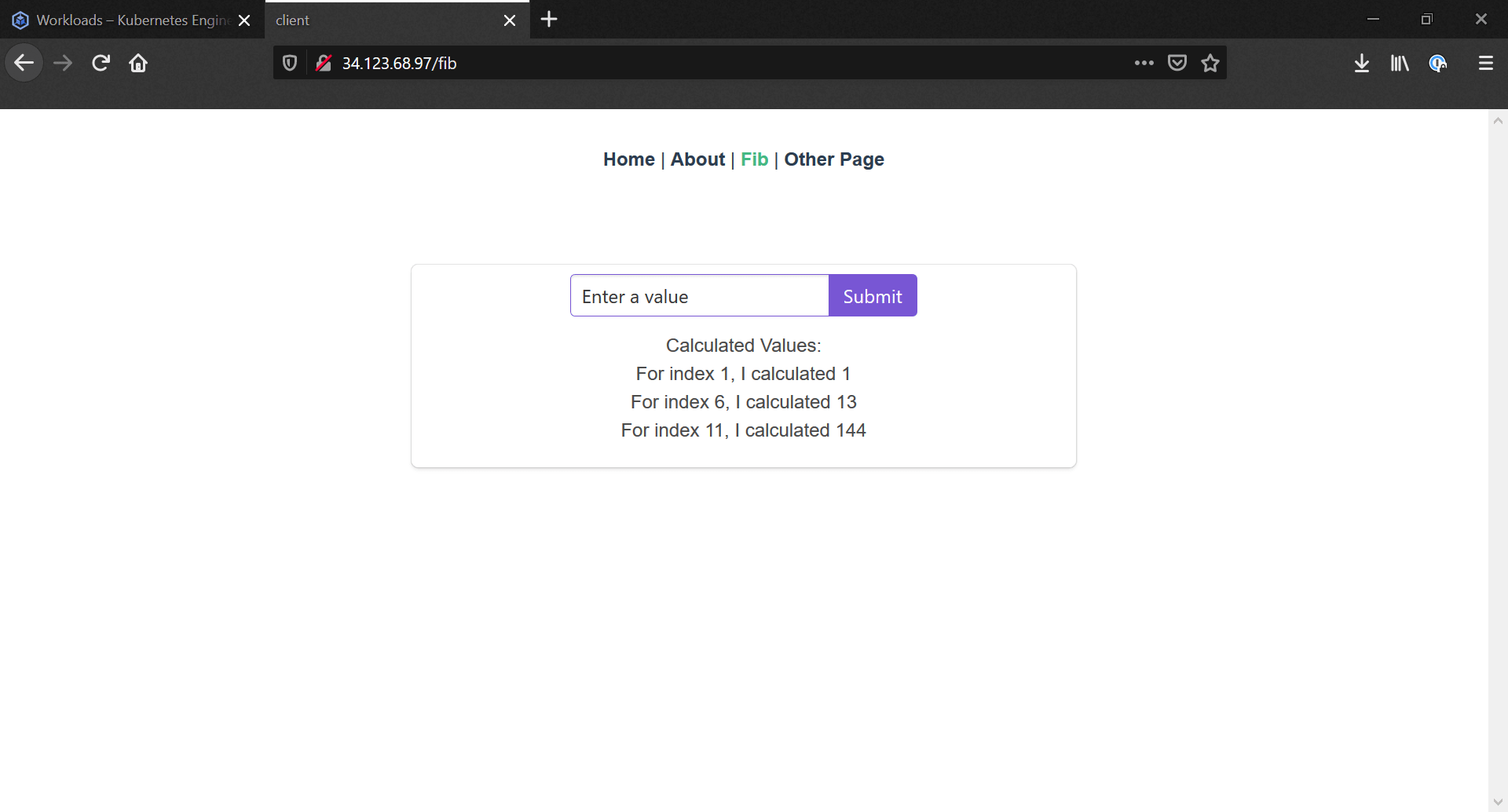
If we wanted to set up an actual web address, we'd need to purchase a domain, set the A record as the IP for our external load balancer, and finally set up a certificate manager to handle the https authentication.
Javascript Source(s): mermaid.min.js